Bedbugs
What is a Bedbugs?
Bedbugs are considered pests due to their parasitic nature, feeding on the blood of humans and animals, primarily at night. Their bites can cause itching, allergic reactions, and psychological stress. Infestations can occur rapidly as bedbugs are excellent hitchhikers, traveling on luggage, clothing, and furniture. Their resilience and ability to hide in cracks and crevices make them difficult to eliminate, leading to long-term infestations. Bedbugs are particularly problematic in homes, hotels, and other shared accommodations, where they disrupt comfort and hygiene.
- Bedbugs feed exclusively on blood and are most active during nighttime, leaving itchy welts on their hosts.
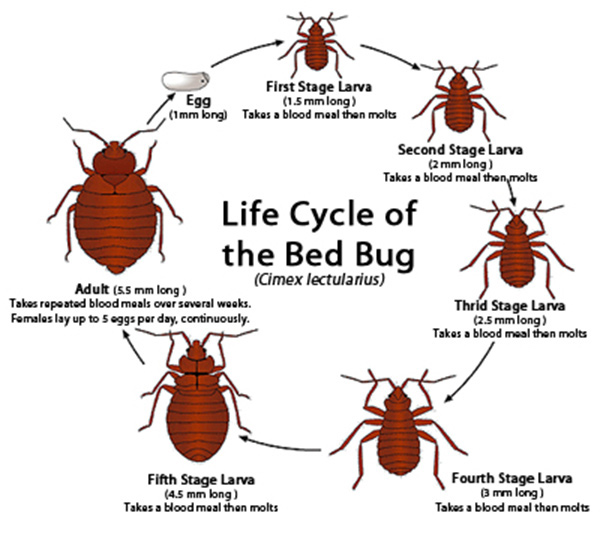
- A single female bedbug can lay up to 500 eggs in her lifetime, with eggs hatching in 6-10 days and maturing into adults within a month under favorable conditions.
- Bedbugs typically stay within a few meters of their hosts but can spread through luggage, furniture, and clothing to new locations.
- Bedbugs hide in cracks, mattresses, furniture seams, and baseboards during the day, emerging at night to feed. They can survive for months without feeding, making eradication challenging.